V Fib Pulseless V Tach Algorithm

Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
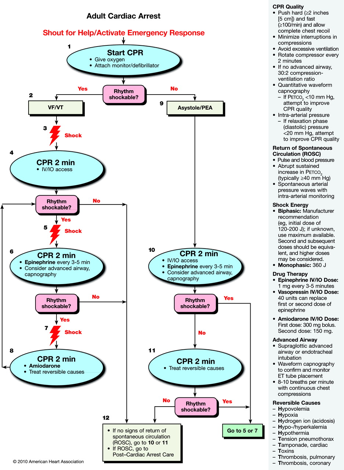
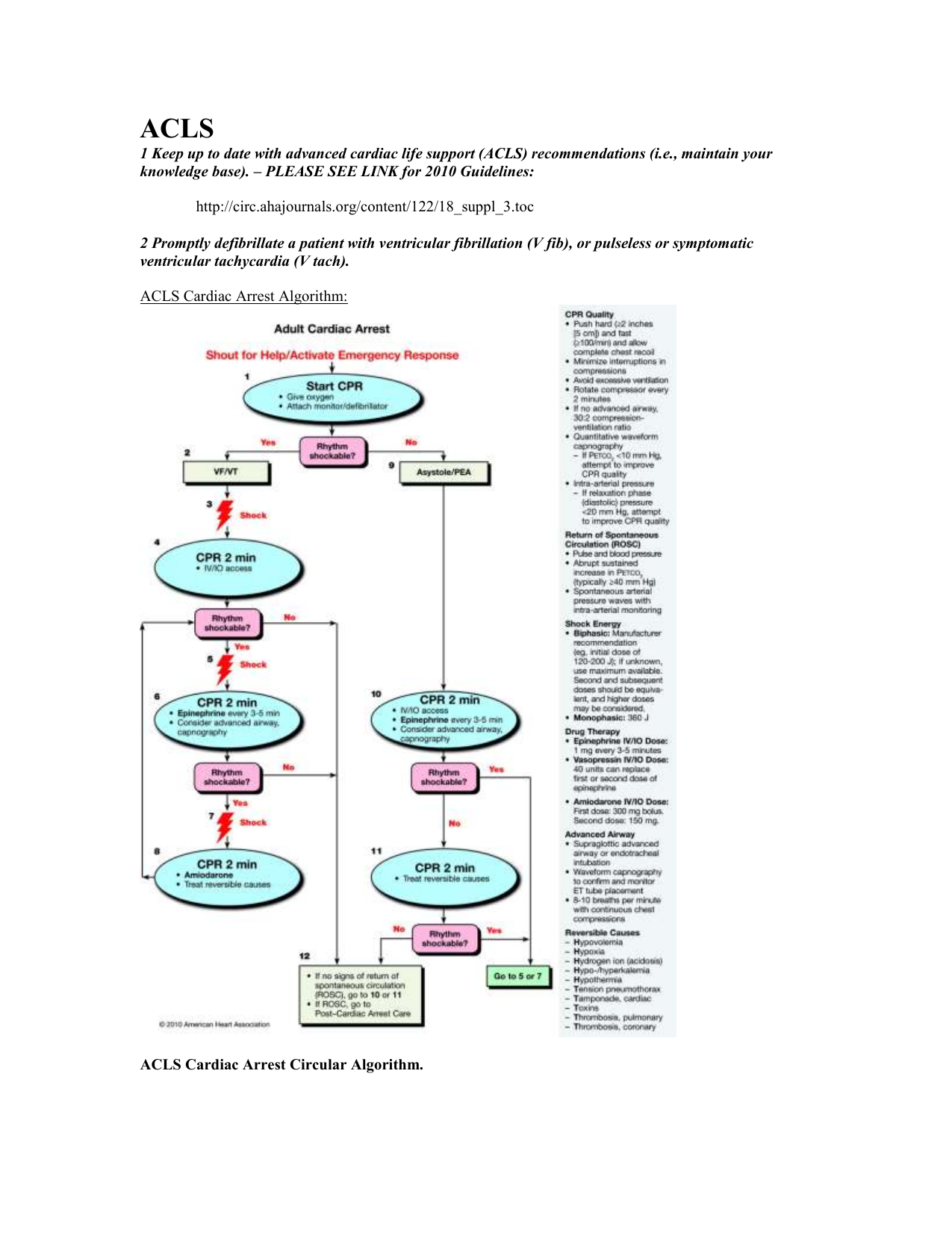
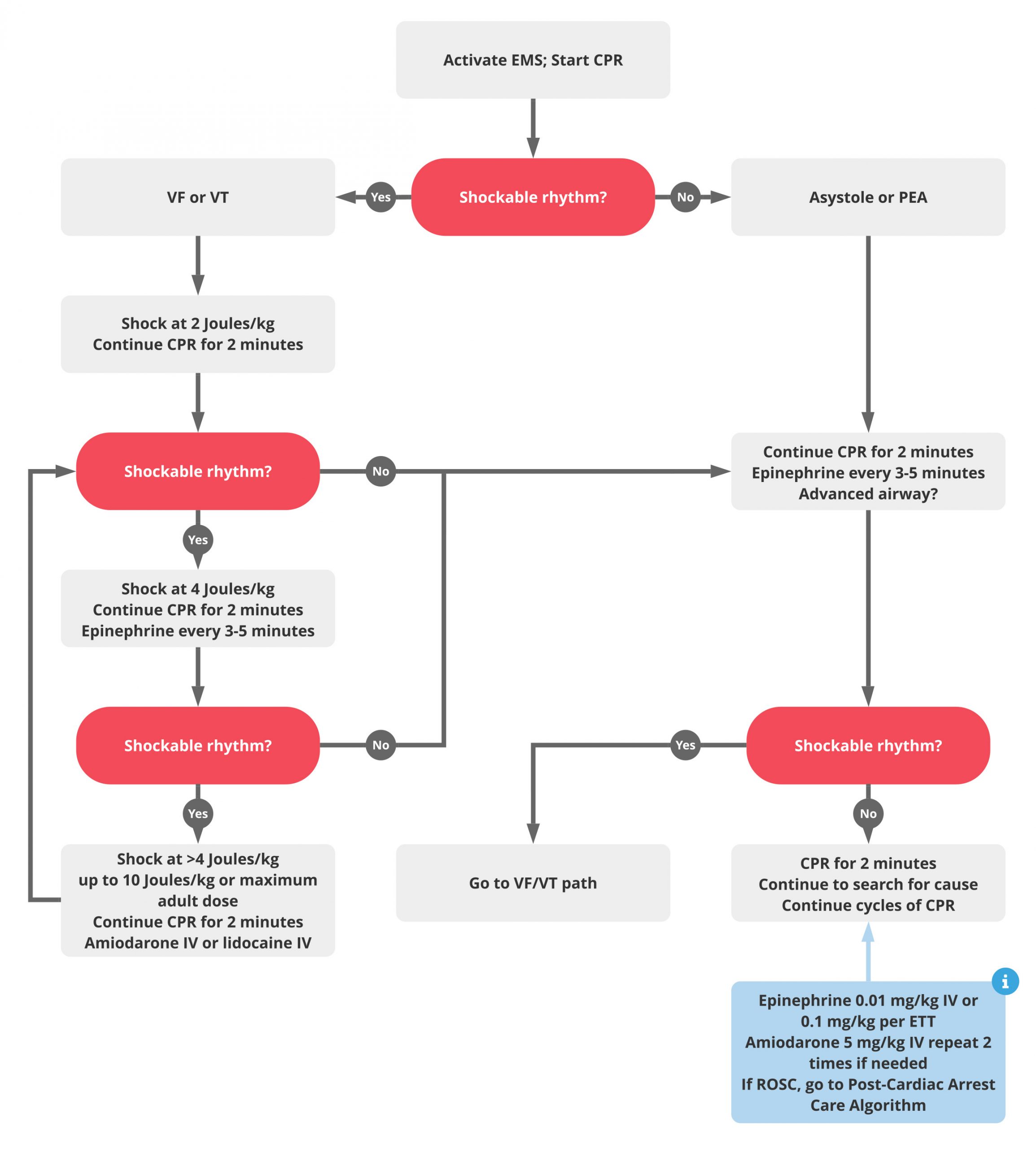
V fib pulseless v tach algorithm. One shock defibrillate 120 to 200joules biphasic or 360joules monophasic one time if still in v. Pals cardiac arrest algorithm 1. Cpr 2 min. Administer high quality cpr for 2 minutes 3.
If diastolic pressure during cpr with an arterial line is 20 mmhg then cpr quality needs to improve. Ventricular fibrillation is a shockable rhythms and is treated in a similarly to ventricular tachycardia vt. The pulseless ventricular tachycardia rhythm is primarily identified by several criteria. First the rate is usually greater than 180 beats per minute and the rhythm generally has a very wide qrs complex.
Asystole and pea are also included in the cardiac arrest algorithm but are non shockable rhythms. Administer shock at 2 joules kg 2. Check rhythm if not shockable move to asystole pea rhythm protocol if. Rhythm is shockable ventricular fibrillation or unstable ventricular tachycardia 1.
For treatment purposes pulseless vt is treated the same as ventricular fibrillation. The pulseless arrest algorithm has been established as the best practice in treating ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia are treated using the left branch of the cardiac arrest arrest algorithm. The treatment of such an arrhythmia is included in the acls pulseless arrest algorithm.
The emergency response system has been activated. Second the patient will be pulseless. Activate emergency medical services call a pediatric code blue obtain aed or defibrillator 2. The pulseless arrest algorithm follows after the primary survey has already been conducted.
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia vt is included in the algorithm with ventricular fibrillation vf. And third the rhythm originates in the ventricles. Vf and pulseless vt are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion. If the rhythm changes to a v fib or v tach shockable rhythm move to that algorithm and prepare to shock the patient.
If a nonshockable rhythm is present and there is no pulse continue with cpr. If the patient shows signs of return of spontaneous circulation or rosc administer post cardiac care.