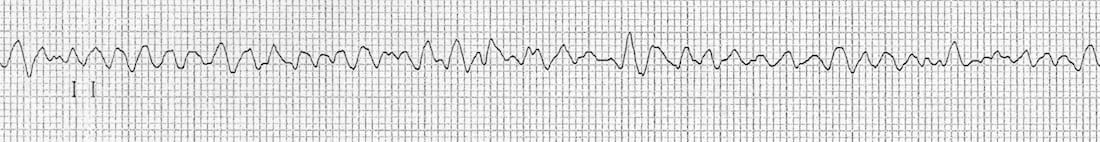
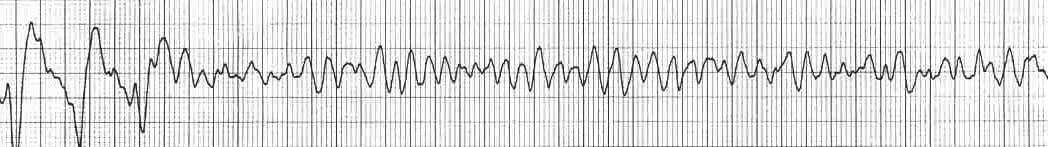
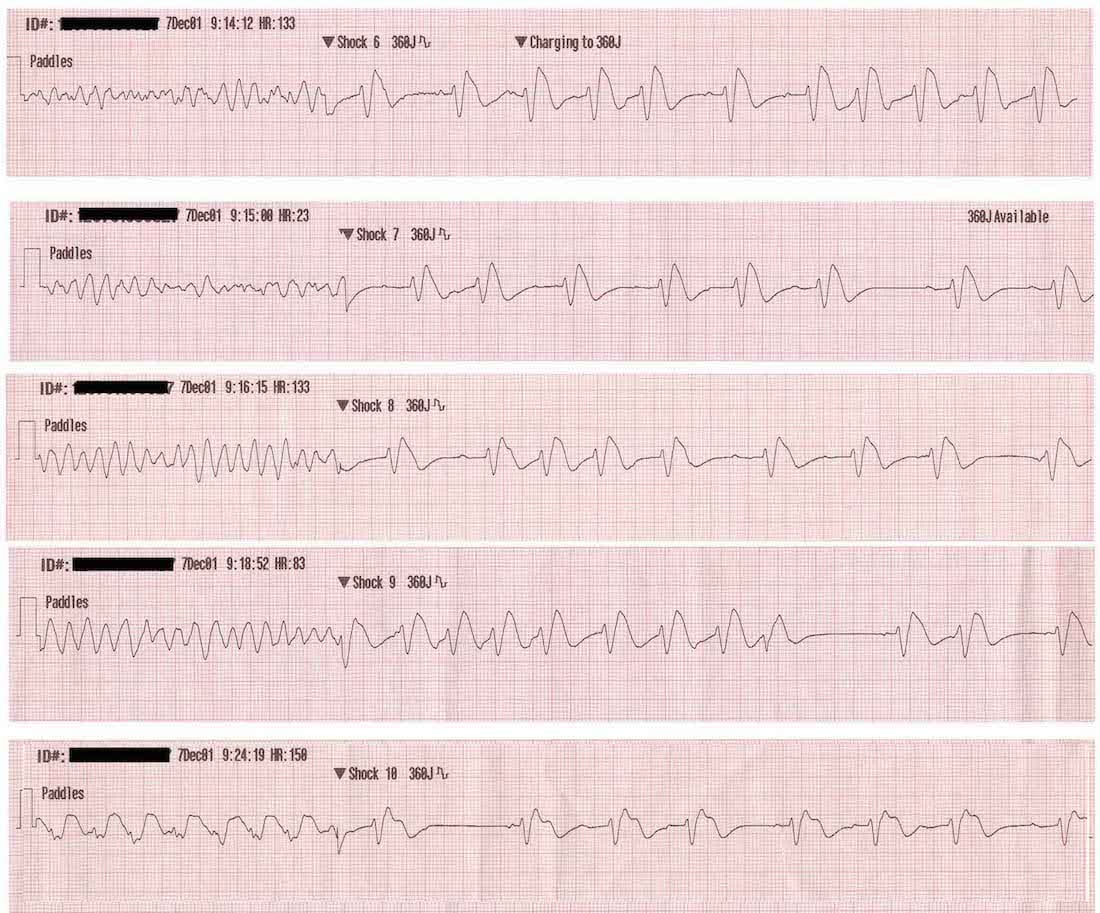
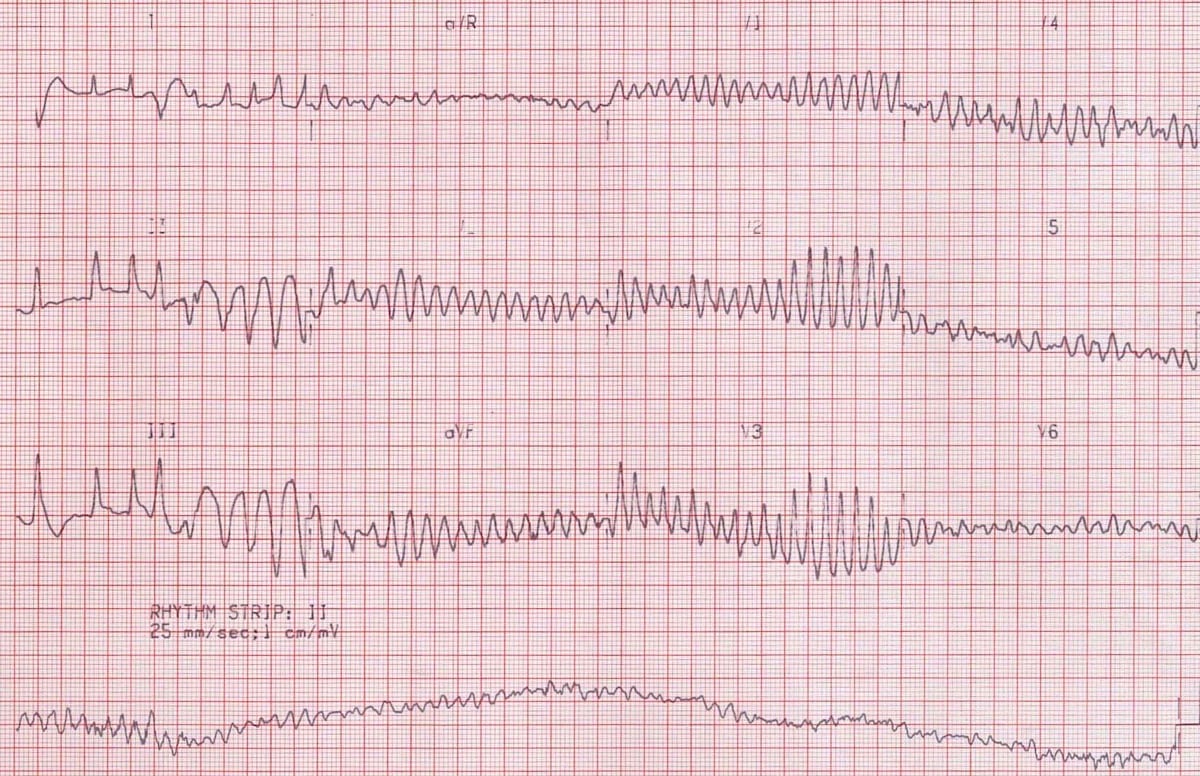
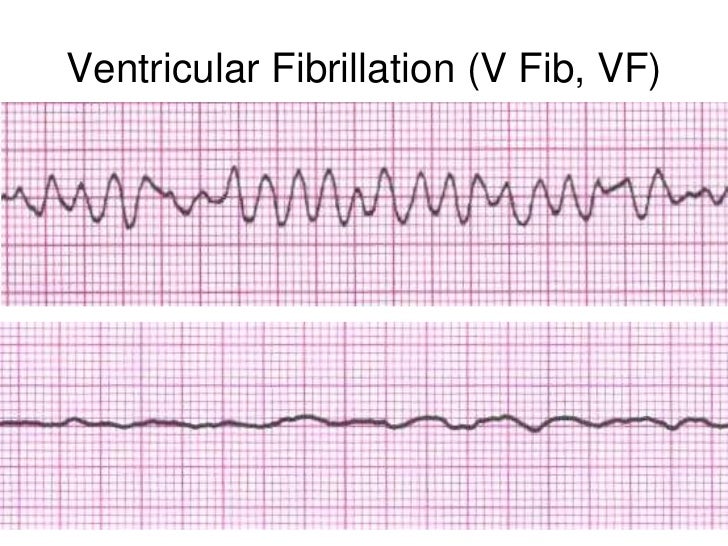
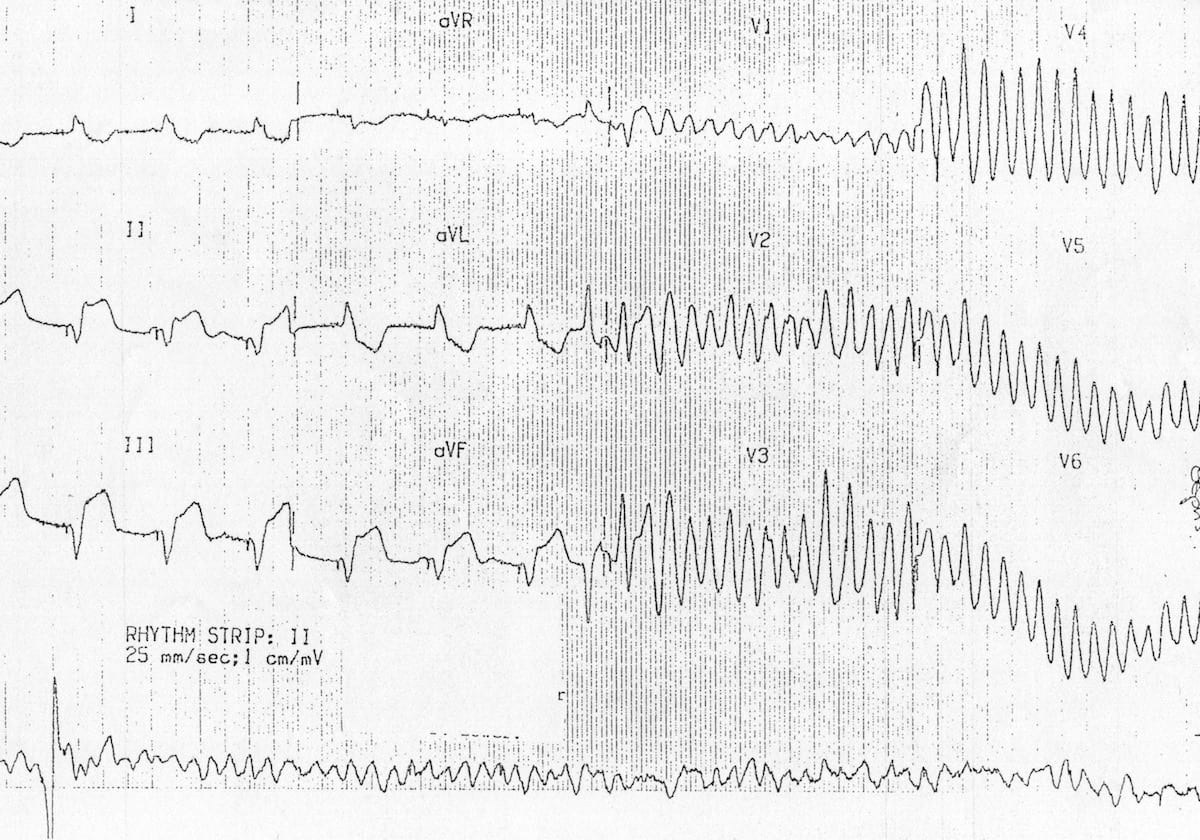
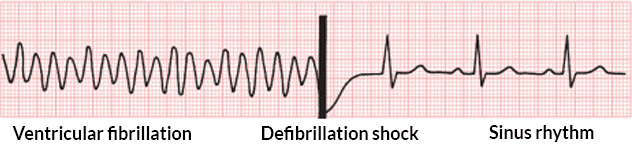
V Fib Rhythm Strip

The electrical impulses do not travel in an orderly fashion through the atria as with normal conduction sinus rhythm.
V fib rhythm strip. However if the rhythm is asystole defibrillation will be ineffective. Symptoms of both afib and vfib are shortness of breath dizziness nausea and chest pain. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation or v fib is considered the most serious cardiac rhythm disturbance.
Ventricular fibrillation v fib or vf is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver instead of pumping normally. Ventricular fibrillation vf is the the most important shockable cardiac arrest rhythm. The course provides training on the key features of an ekg tracing. Vf can rapidly lead to heart muscle ischemia and there is a high likelihood that it will deteriorate into asystole.
As the treatments for asystole and ventricular fibrillation are different it is important to differentiate between the two. Disordered electrical activity causes the heart s lower chambers ventricles to quiver or fibrillate instead of contracting or beating normally. If it is fine v fib you may terminate the rhythm. A fib is the most common type of irregular heart rhythm.
If in doubt it is acceptable to deliver a shock. Ventricular fibrillation vf and pulseless ventricular tachycardia vt are life threatening cardiac rhythms that result in ineffective ventricular contractions. The two images show what ventricular fibrillation will look like on an ekg rhythm strip. Vf figure 24 is a rapid quivering of the ventricular walls that prevents them from pumping.
The ventricles suddenly attempt to contract at rates of up to 500 bpm. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. Atrial fibrillation afib and ventricular fibrillation vfib are both a type of abnormal heart rhythm arrhythmia. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10 of.
A good starting point for learning about v fib and other types of ekg interpretation is our ekg basics training course. Instead in several areas inside the atria form groups of excitable cells generate electrical impulses that fire simultaneously and spread throughout the atria causing a short circuiting effect see above. This prohibits the heart from pumping blood causing collapse and cardiac arrest. This rapid and irregular electrical activity renders the ventricles unable to contract in a synchronised manner resulting in immediate loss of cardiac output.
These features include observing p wave forms measurement of ekg intervals and segments assessment of rhythm calculating heart rate and the evaluation of other relevant wave segments. To focus on a specific arrhythmia category use the buttons below. For each arrhythmia we include a sample rhythm strip as well as a summary of important attributes. Atrial fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the atria and ventricular fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the ventricles.