V Fib Treatment Pals

Administer high quality cpr for 2 minutes 3.
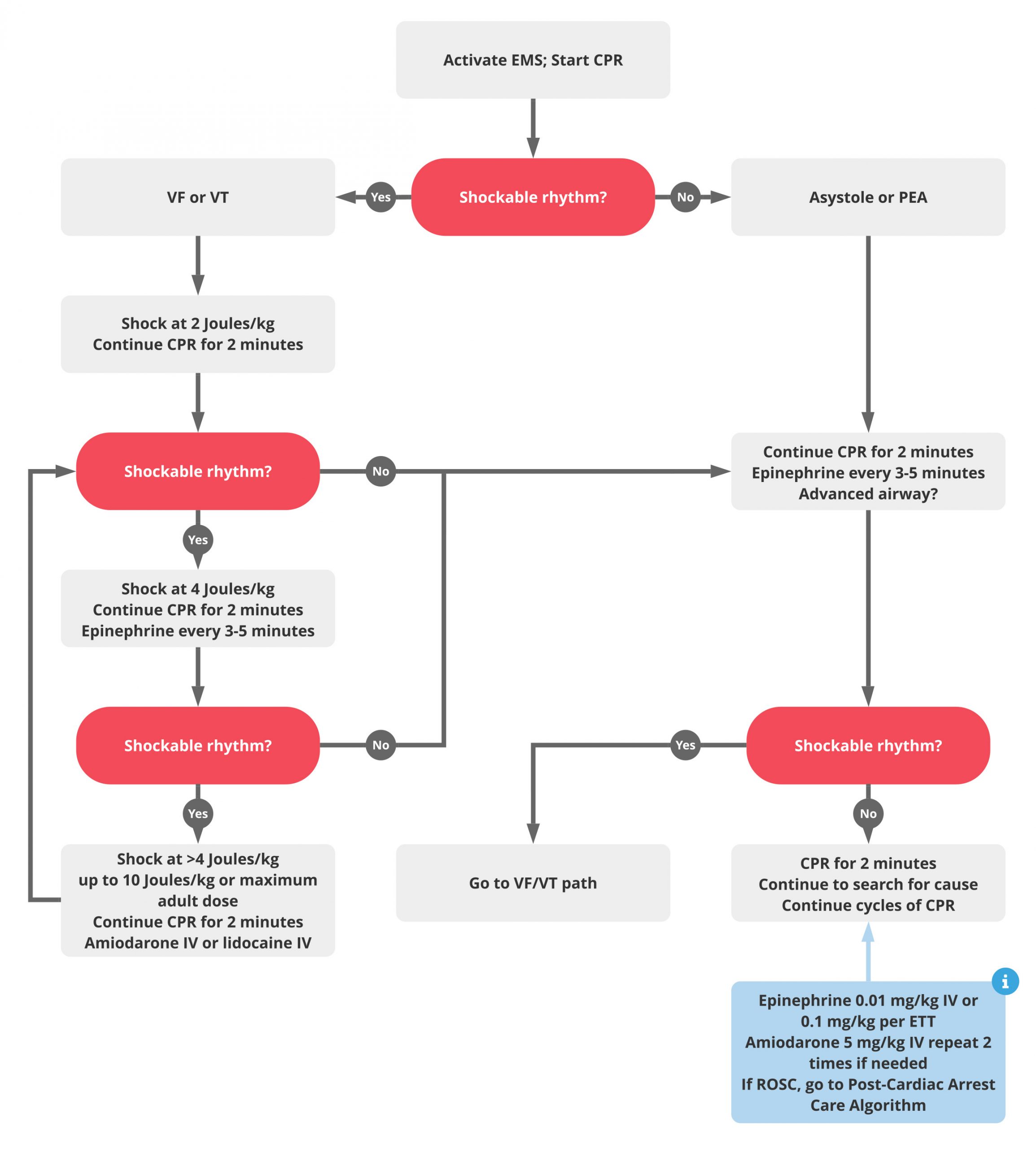
V fib treatment pals. Age category age range normal heart rate newborn 0 3 months 80 205 per minute infant young child 4 months to 2 years 75 190 per minute child school age 2 10 years 60 140 per minute older child adolescent. Asystole and pea are also included in the cardiac arrest algorithm but are non shockable rhythms. Is the rhythm shockable. Tachycardia is diagnosed by manual testing or heart rate monitor normal heart rates vary with age size.
5 mg kg over 20 60 minutes max dose. 5 mg kg bolus max dose. A 15 year old presents after collapsing at a sporting event. Deliver rescue breaths d.
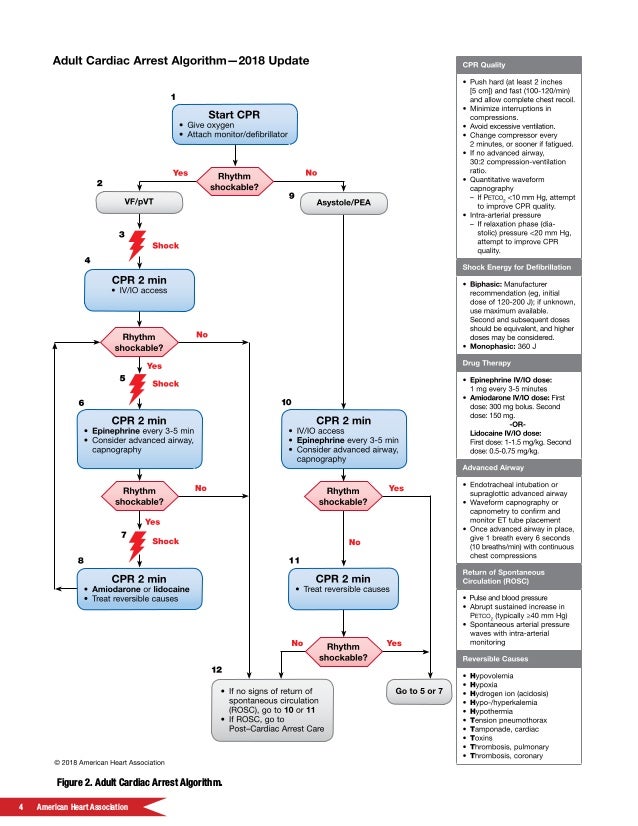
Initial rhythm demonstrates the following. Vf and pulseless vt are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion. Administer shock at 2 joules kg 2. Ventricular fibrillation v fib recurrent hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia hypertrophic cardiomyopathy supraventricular tachyarrhythmias svt dose.
Activate emergency medical services call a pediatric code blue obtain aed or defibrillator 2. Consider halting pals efforts in people who have had prolonged asystole. Used to treat atrial fibrillation atrial flutter atrial tach and symptomatic vt. If the patient still has an svt rhythm 1 2 minutes later give 12mg iv io over 1 3 seconds immediately followed by 20ml of ns by rapid ivp io.
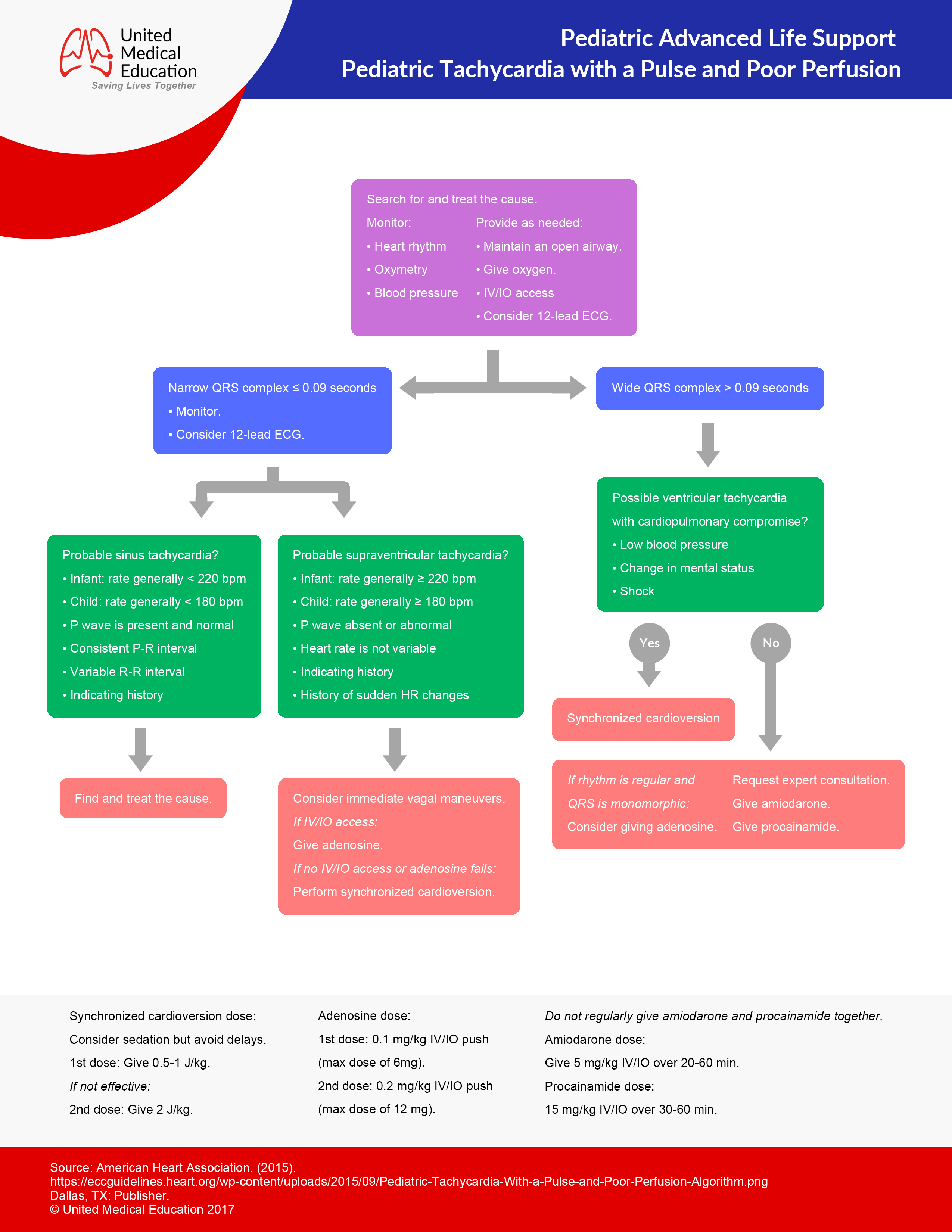
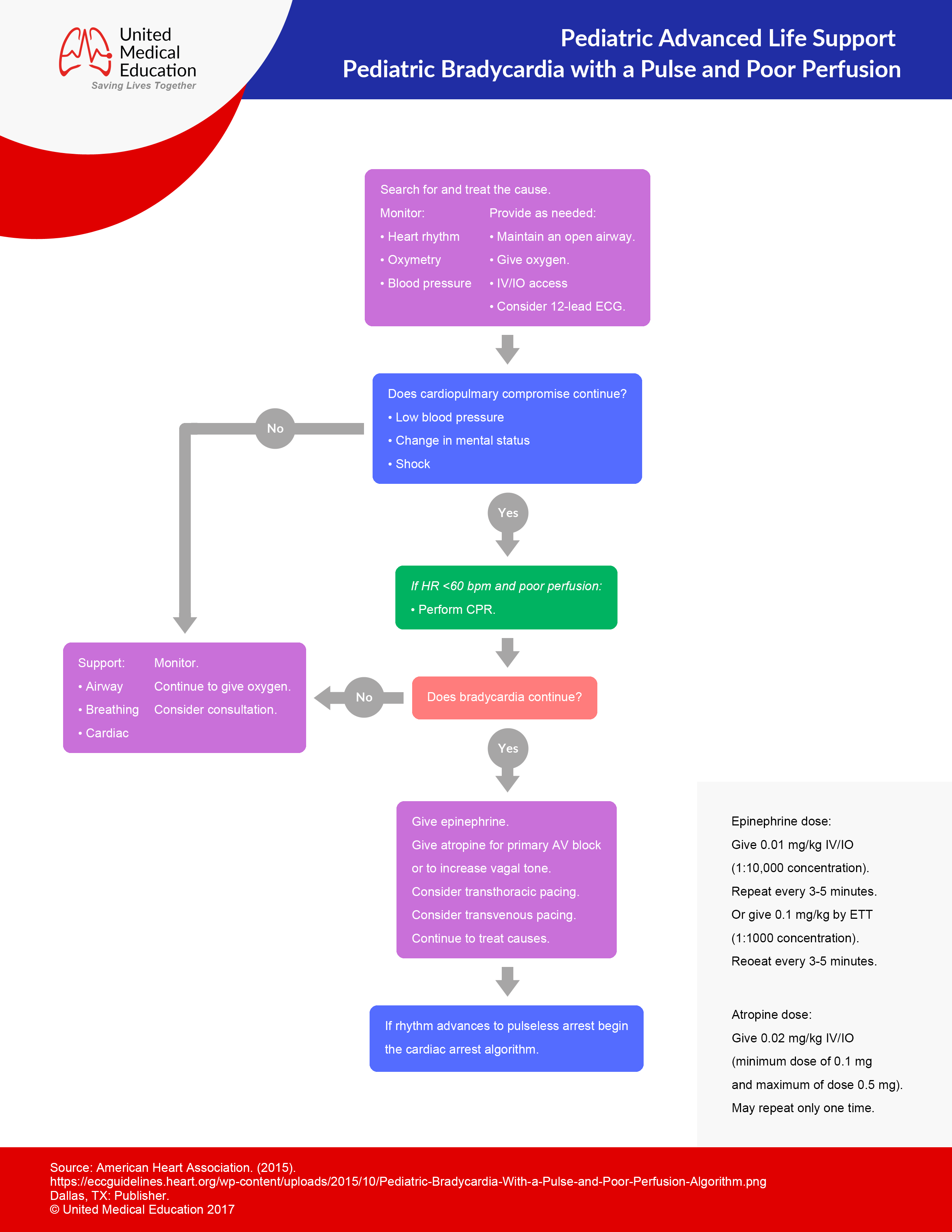
Doses should be administered and followed with a rapid flush as fast as possible. Pals tachycardia initial management algorithm 1. Instructional guide for pediatric advanced life support training and medications. What is your initial step in management.
The treatment of vf and pulseless vt ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia is included in the cardiac arrest algorithm. Pals cardiac arrest algorithm 1. 300 mg vt svt. If patient fails to respond to stimulus and treatment.
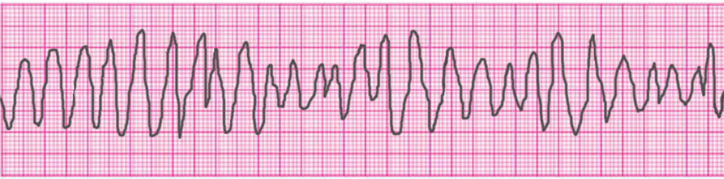
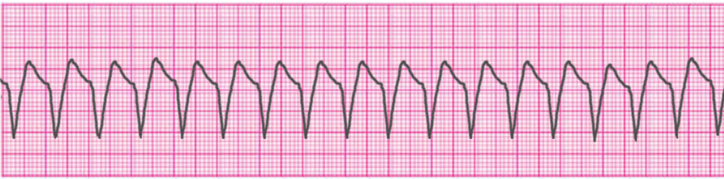
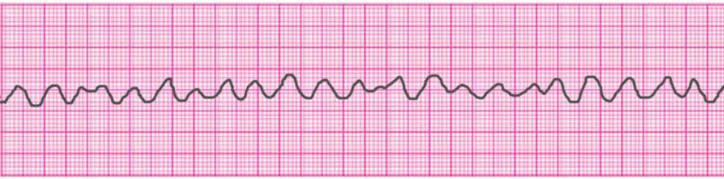
You are at the gym and witness a 16 year old on the treadmill slump to the ground. Ventricular fibrillation vf or v fib is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest ohca and the most salvageable one. You rush to assess the person and find them to be pulseless and not breathing. Pulseless vt v fib.
It is inappropriate to provide a shock to pulseless electrical activity or asystole. Consider a lower dose of 3mg for patients that. Rapid infusion causes hypotension. Apply an aed c.
Call for help initiate cpr b. Check rhythm if not shockable move to asystole pea rhythm protocol if. 5 in vf the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non ischemic arrhythmia. Ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
Give 6mg iv io over 1 3 seconds immediately followed by 20ml of ns by rapid iv io. 8 although vf appears as a chaotic and disorganized rhythm characteristics of the ventricular fibrillation waveform such as.