V Fib V Tach Ecg

Distinguishing between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation from compressed ecg signal in wireless body sensor networks annu int conf ieee eng med biol soc.
V fib v tach ecg. A wide range of conditions may cause ventricular tachycardia and the ecg is as nuanced as are those conditions. A good starting point for learning about v fib and other types of ekg interpretation is our ekg basics training course. Ventricular fibrillation is treated according to the resuscitation algorithm. Treatment of ventricular fibrillation.
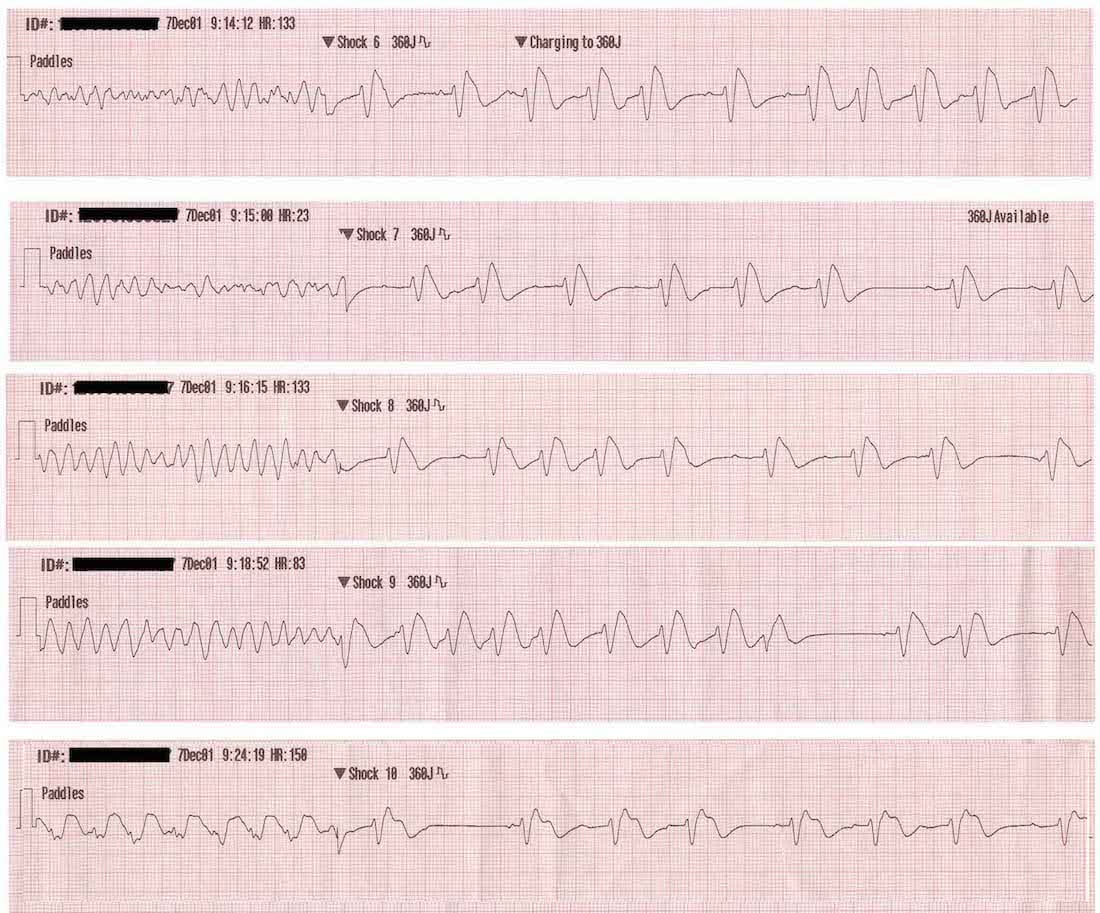
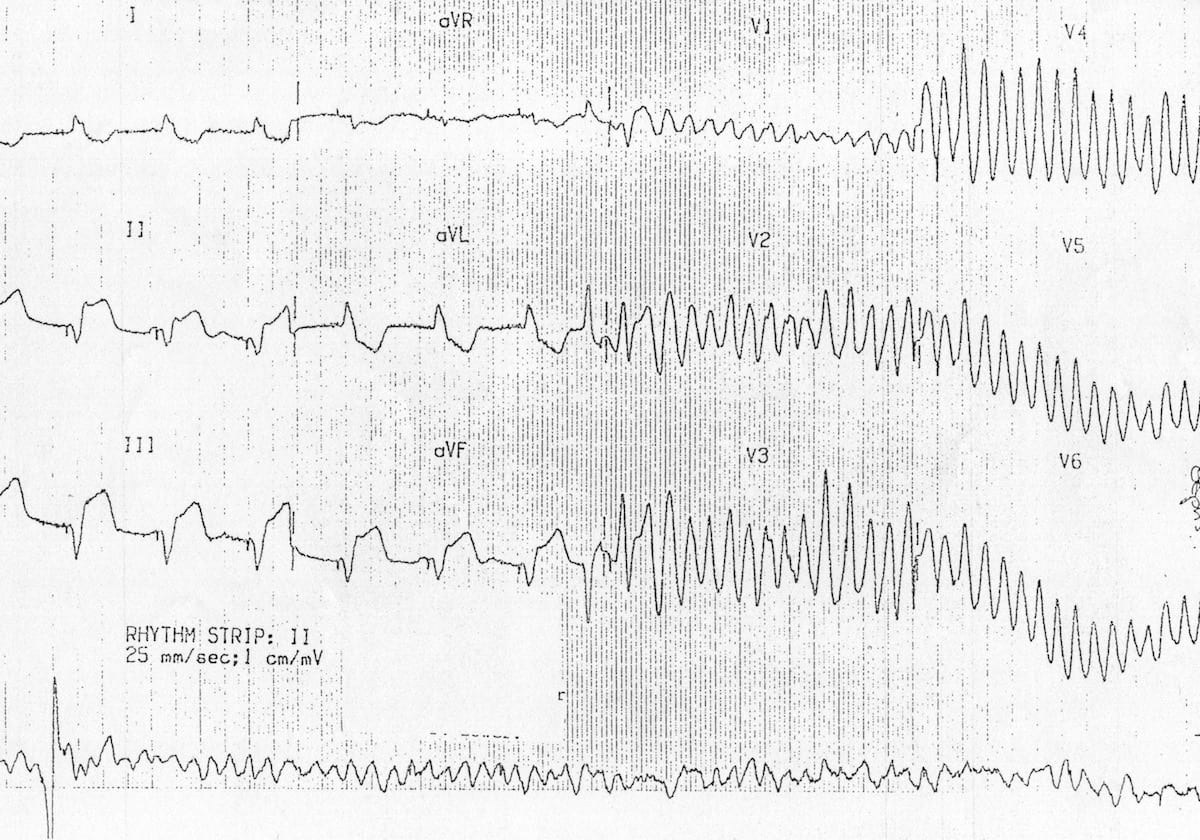
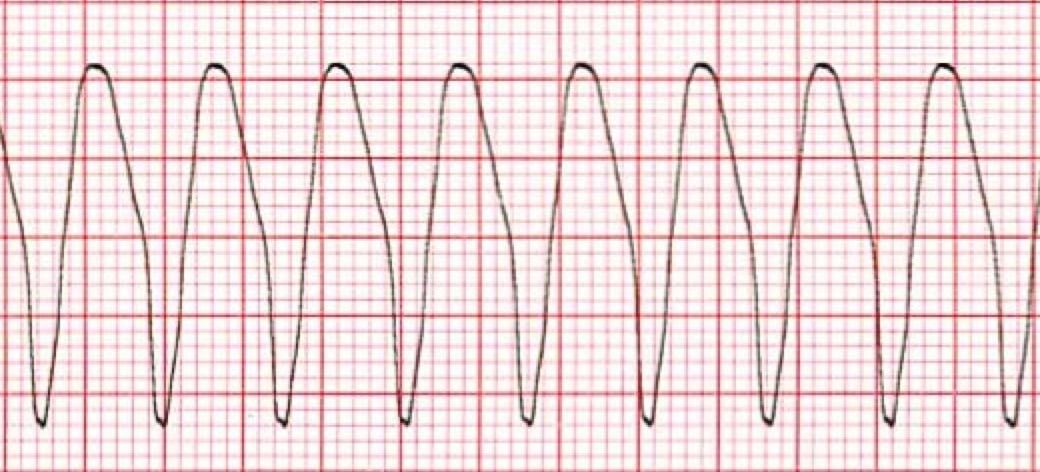
Ecg showing ventricular tachycardia degenerating into ventricular fibrillation. By bagnall et al. Acls cardiac arrest vtach and vfib algorithm perform the initial assessment perform high quality cpr establish an airway and provide oxygen to keep oxygen saturation 94 monitor the victim s heart rhythm and blood pressure if the patient is in vtach or vfib this is a shockable rhythm apply defibrillator pads or paddles and shock the. They are atrial tachycardia monofocal or multifocal atrial fibrillation atrial flutter atrioventricular nodal re entry tachycardia atrioventricular re entry.
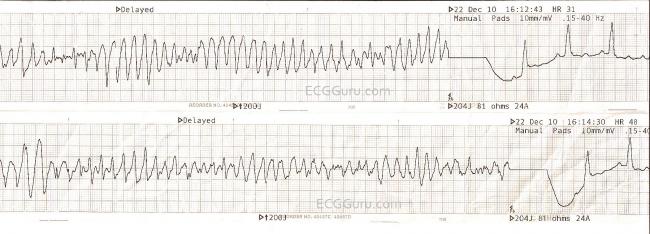
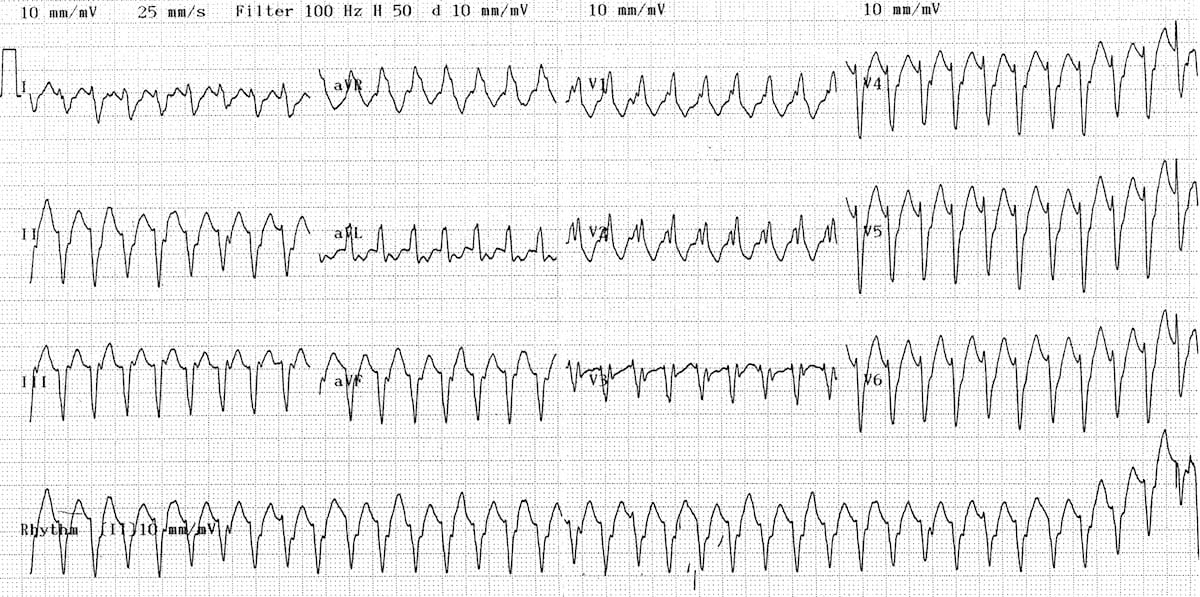
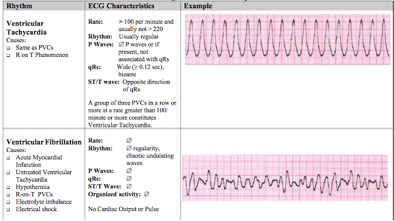
Ventricular tachycardia vs ventricular fibrillation arrhythmia means irregular cardiac rhythm and slow arrhythmias are called bradyarrhythmias and fast ones are called tachyarrhythmias there are various types of arrhythmias. This rhythm usually appears on the monitor as a wide regular and very rapid rhythm. Regardless of etiology and ecg ventricular tachycardia is always a potentially life threatening arrhythmia which requires immediate attention. Ventricular tachycardia v tach typically responds well to defibrillation.
The course provides training on the key features of an ekg tracing. Cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death. Bmc medical genetics 15 2014. Ventricular tachycardia is a highly nuanced arrhythmia which originates in the ventricles.
Although a few seconds may not result in problems longer periods are dangerous. Short periods may occur without symptoms or present with lightheadedness palpitations or chest pain. These features include observing p wave forms measurement of ekg intervals and segments assessment of rhythm calculating heart rate and the evaluation of other relevant wave segments. Differences between patients with ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation as assessed by signal averaged electrocardiogram radionuclide ventriculography and cardiac mapping.
Patients may present with or without a pulse.