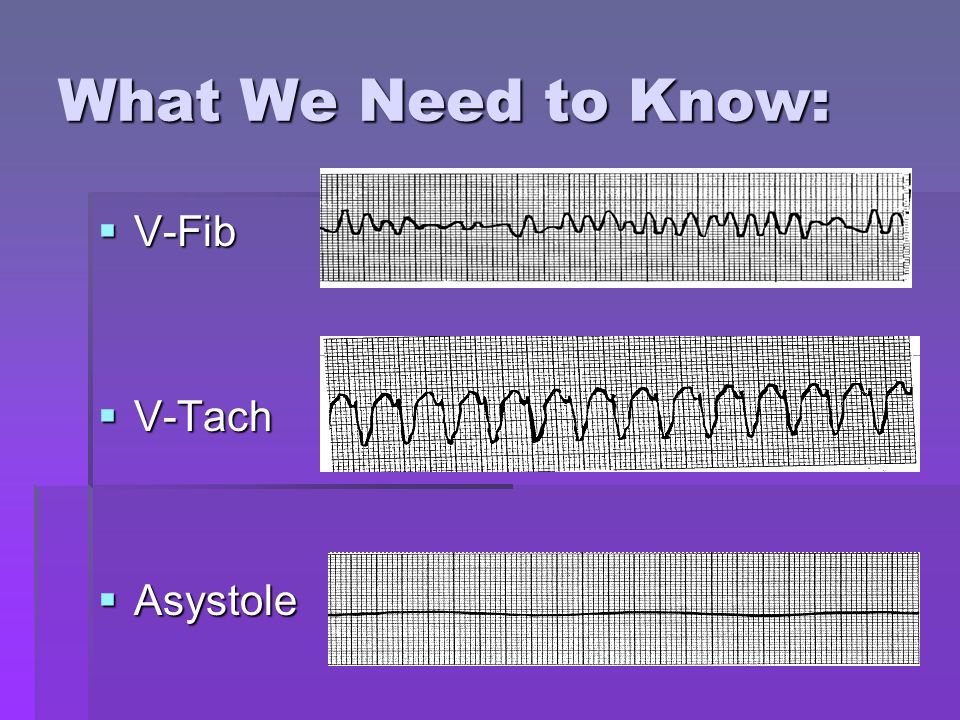
V Fib Vs Pulseless V Tach

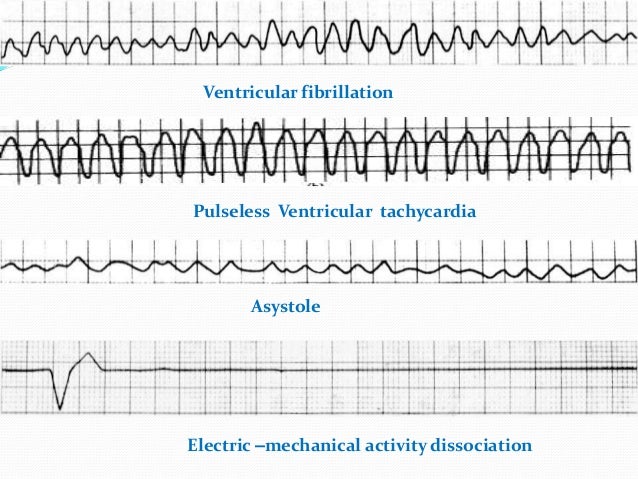
Asystole and pea are also included in the cardiac arrest algorithm but are non shockable rhythms.
V fib vs pulseless v tach. And third the rhythm originates in the ventricles. Patients may present with or without a pulse. Ventricular fibrillation pulseless electrical activity pea and sudden cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation vfib electrocardiogram ecg blood tests.
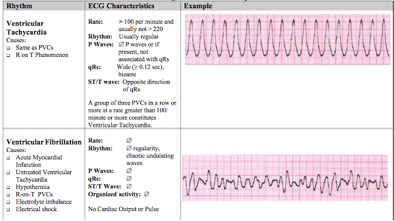
Vf figure 24 prevents the ventricular walls from pumping as it causes a rapid quivering and this motion doesn t synchronize with atrial contractions. Ventricular tachycardia vs ventricular fibrillation arrhythmia means irregular cardiac rhythm and slow arrhythmias are called bradyarrhythmias and fast ones are called tachyarrhythmias there are various types of arrhythmias. Coronary catheterization angiogram cardiac computerized tomography ct magnetic resonance imaging mri summary of v tach and v fib. Ventricular tachycardia is a poorly perfusing rhythm.
Ventricular fibrillation vf and pulseless ventricular tachycardia vt are life threatening cardiac rhythms that result in ineffective ventricular contractions. The ventricular motion of vf is not synchronized with atrial contractions. Quickly memorize the terms phrases and much more. Ventricular tachycardia v tach typically responds well to defibrillation.
Ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia are treated using the left branch of the cardiac arrest arrest algorithm. The points of difference between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Vf and pulseless vt are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion. This article will focus on ventricular fibrillation pulseless electrical activity and sudden cardiac arrest.
This rhythm usually appears on the monitor as a wide regular and very rapid rhythm. Have been summarized below. The pulseless ventricular tachycardia rhythm is primarily identified by several criteria. Vf figure 24 is a rapid quivering of the ventricular walls that prevents them from pumping.
They are atrial tachycardia monofocal or multifocal atrial fibrillation atrial flutter atrioventricular nodal re entry tachycardia atrioventricular re entry. Second the patient will be pulseless.