Ventricular Fibrillation V Tach Ekg

No heart rate can be observed.
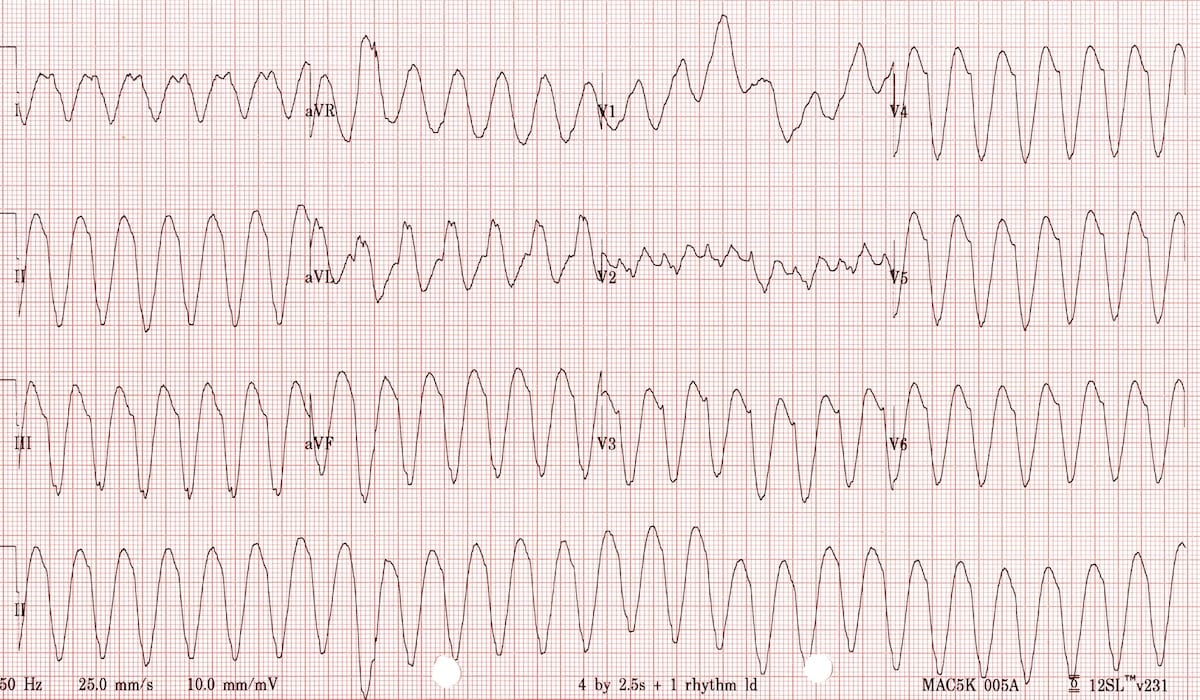
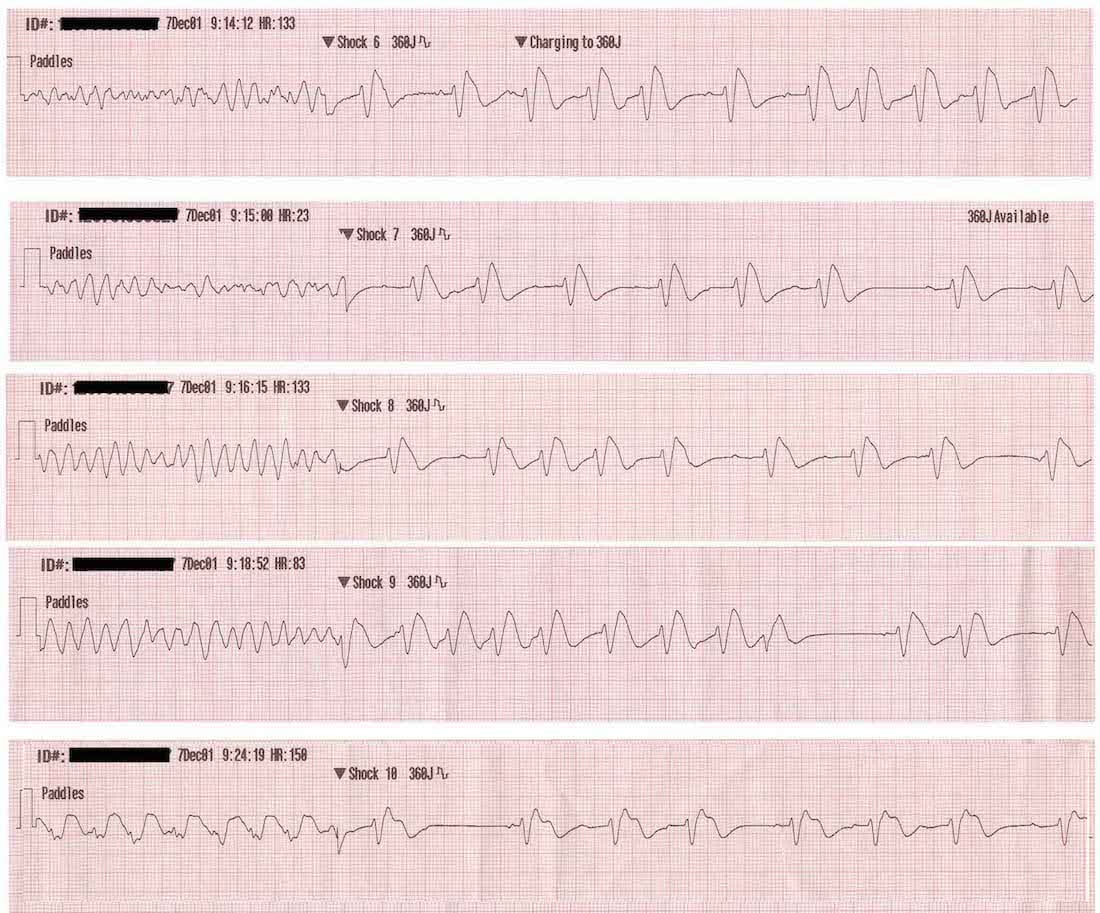
Ventricular fibrillation v tach ekg. Ventricular fibrillation is an emergency condition requiring immediate action. However on closer inspection there are signs of av dissociation with superimposed p waves visible in v1. They are atrial tachycardia monofocal or multifocal atrial fibrillation atrial flutter atrioventricular nodal re entry tachycardia atrioventricular re entry. This rapid and irregular electrical activity renders the ventricles unable to contract in a synchronised manner resulting in immediate loss of cardiac output.
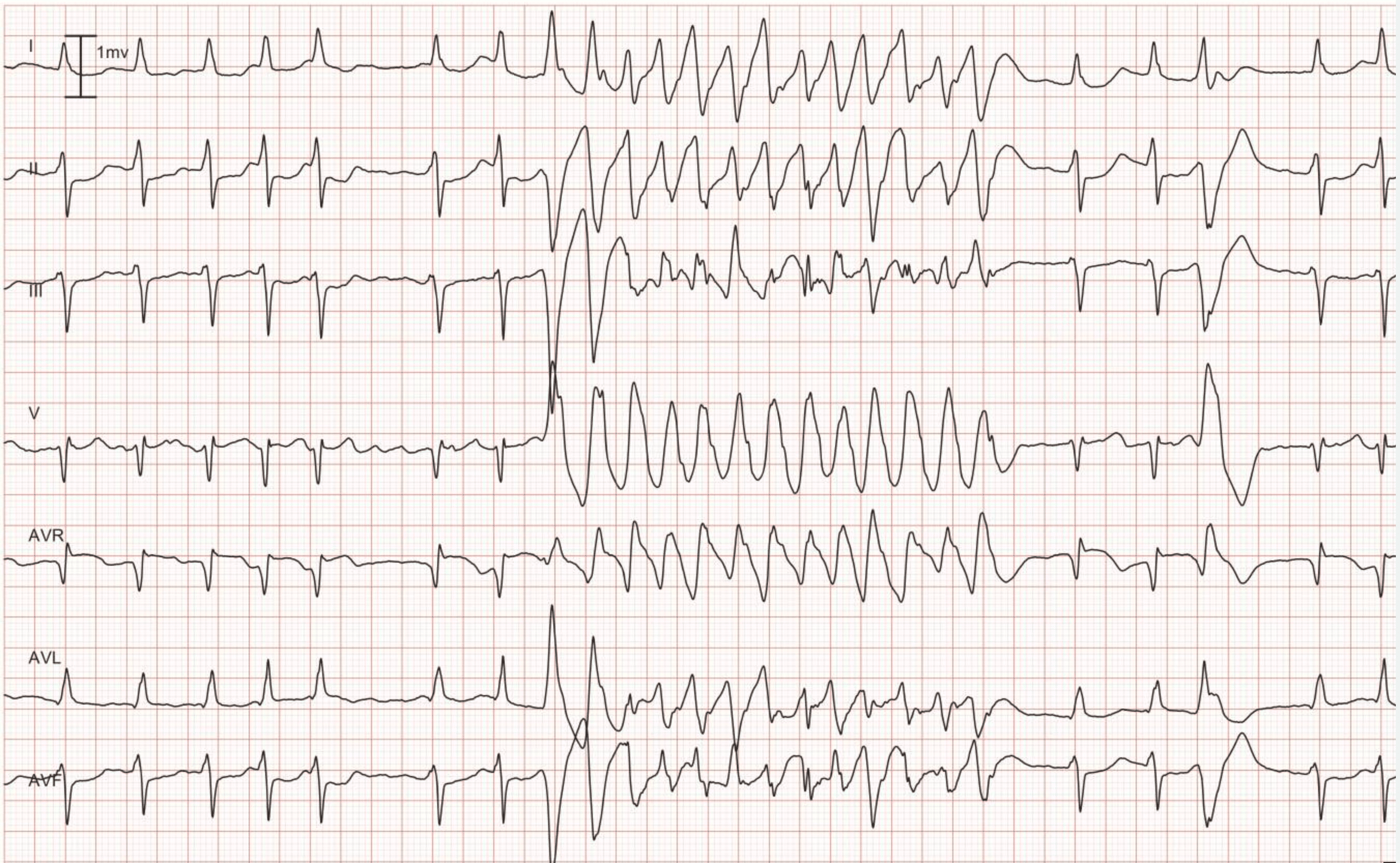
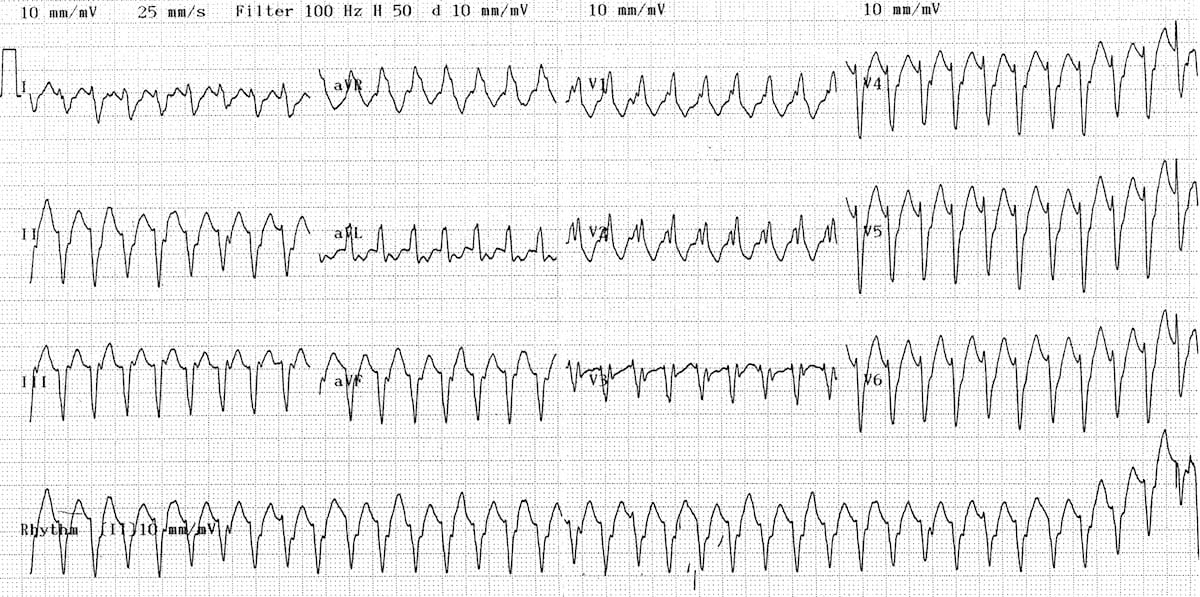
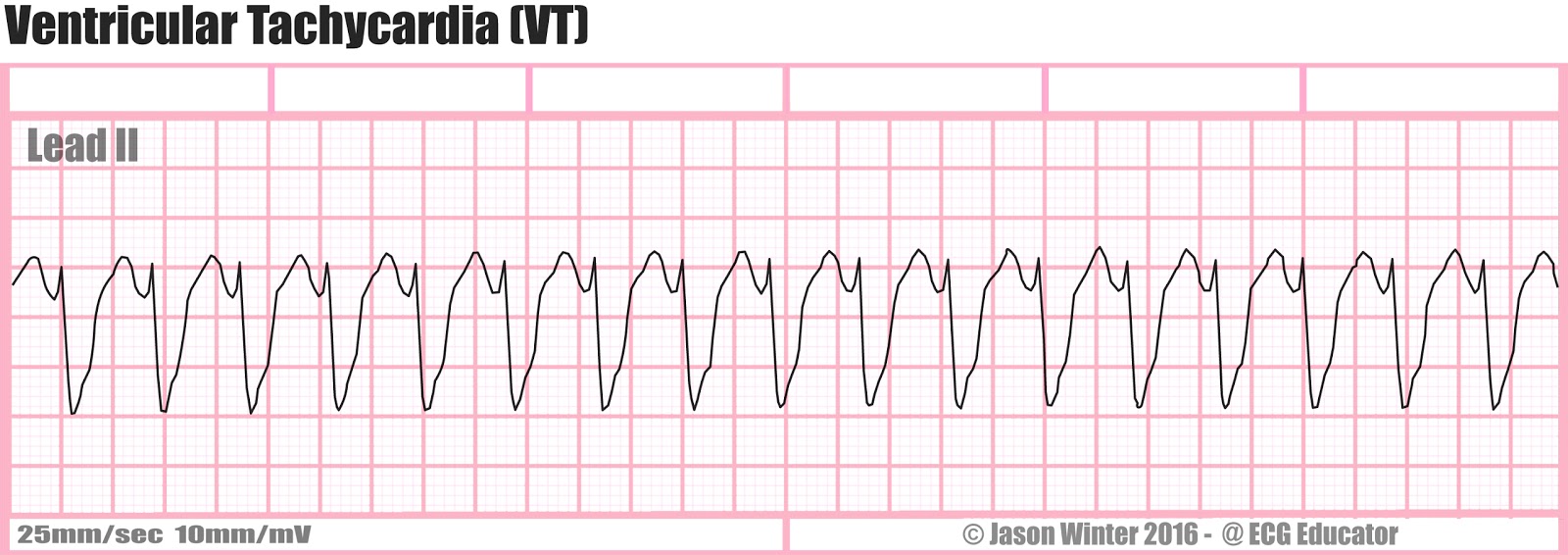
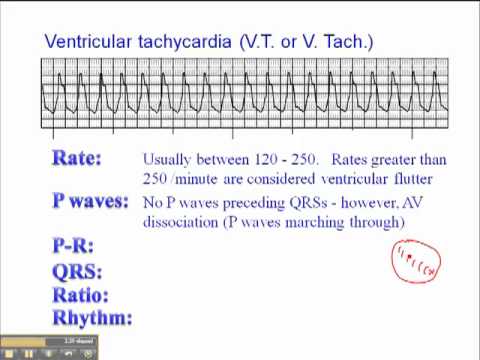
No normal ekg waves are present. Ventricular tachycardia v tach or vt is a type of regular and fast heart rate that arises from improper electrical activity in the ventricles of the heart. Ventricular tachycardia with rate 100 to 120 beats per minute is referred to as slow ventricular tachycardia. Ventricular arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms originating in the ventricles that are the leading cause of sudden cardiac death.
Although a few seconds may not result in problems longer periods are dangerous. Journal of the american college of cardiology 11 2 276 283. Ventricular tachycardia vs ventricular fibrillation arrhythmia means irregular cardiac rhythm and slow arrhythmias are called bradyarrhythmias and fast ones are called tachyarrhythmias there are various types of arrhythmias. The ecg allows for subclassification of ventricular tachycardia.
Ventricular fibrillation ventricular fibrillation originates in the ventricles and it chaotic. Distinguishing between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation from compressed ecg signal in wireless body sensor networks annu int conf ieee eng med biol soc. Ventricular arrhythmias pvc s v tach v fib. Types of ventricular tachycardia.
Ventricular tachycardia with rate 250 beats per minute is referred to as ventricular flutter. Short periods may occur without symptoms or present with lightheadedness palpitations or chest pain. Wide qrs complexes qrs duration 0 12 s. Differences between patients with ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation as assessed by signal averaged electrocardiogram radionuclide ventriculography and cardiac mapping.
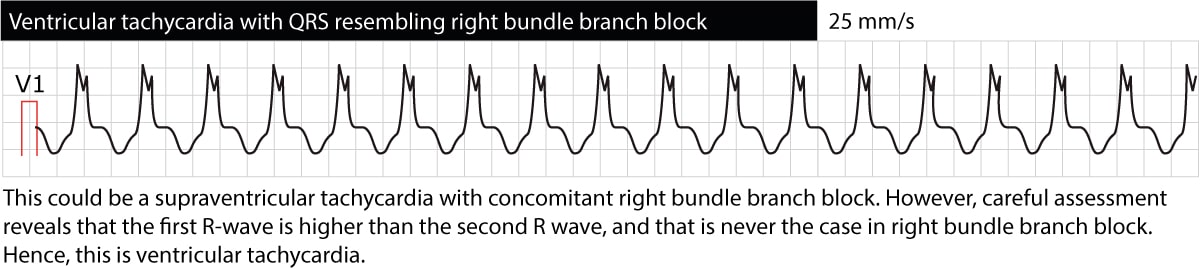
This ecg is a difficult one. The ventricles suddenly attempt to contract at rates of up to 500 bpm.