Vitamin K Dependent Coagulation Factors Include

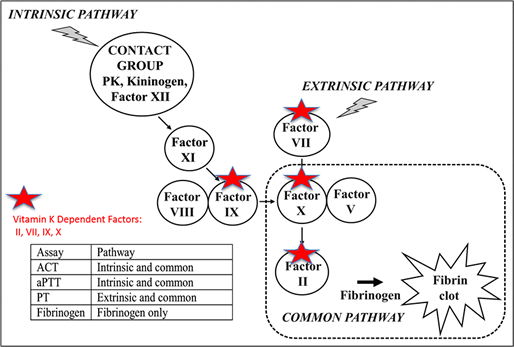
Deficiency of the vitamin k dependent clotting factors vkcfd is a recessive bleeding disorder where problems arise with the four clotting factors i ii vii ix and x.
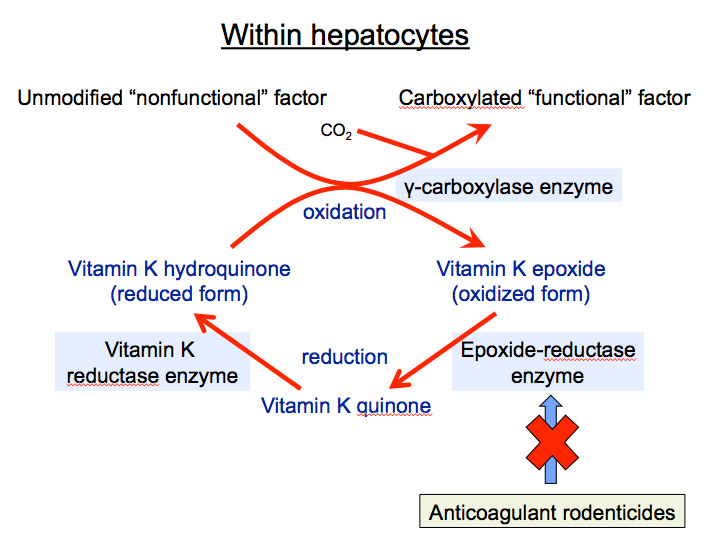
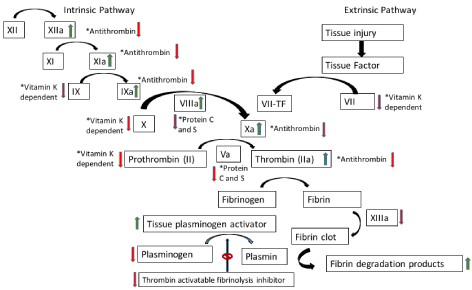
Vitamin k dependent coagulation factors include. Vitamin k serves as an essential cofactor for a carboxylase that catalyzes carboxylation of glutamic acid residues on vitamin k dependent proteins. Substrates include blood clotting proteins bone proteins cell signaling and receptor proteins. The vitamin k dependent protein family includes the zymogen procoagulant factors vii ix x and prothrombin and the anticoagulants protein c protein s and protein z fig. Vitamin k dependent proteins synthesized in the liver play a central role in blood coagulation through either procoagulant or anticoagulant mechanisms.
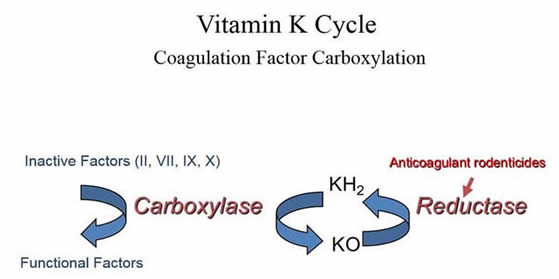
Familial multiple coagulation factor deficiency is rare. Vitamin k deficiency or utilization disorders may affect the γ carboxylation of glutamate and thus the γ carboxyglutamyl glutamic acid residue in these coagulation factors could not form 1 2 vitamin k dependent coagulopathy is characterized by decreased activity of coagulation factors and coagulation. Factor ii is alternatively named prothrombin. 1 4 known vitamin k dependent proteins involved in coagulation include.
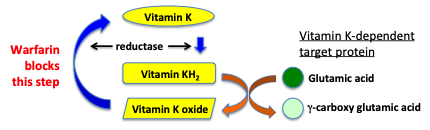
Reviews of vitamin k action and blood coagulation are presented. Warfarin is used in medicine for those at high risk of thromboembolism to prevent the coagulation cascade by reducing vitamin k dependent synthesis of coagulation factors. The key vitamin k dependent proteins include. Also anticoagulation proteins c s and z as well as osteocalcin and the matrix gla protein depend on vitamin k.
Prothrombin alone needs vitamin k to modify 10 different regions within the protein for functionality. Vitamin k can be inhibited by the anticoagulant drug warfarin which acts as an antagonist for vitamin k. Proteins c s and z. When an injury occurs the platelets spread along the injury site and attach to the blood vessel to stop.
Vitamin k dependent coagulation factors include ii vii ix and x. In addition gla is a component of short toxin peptides from the marine snail conus. An equally important role for vitamin k is to activate anticoagulant proteins to control clotting since uncontrolled clotting can be just as dangerous as uncontrolled bleeding. Deficiency of all vitamin k dependent clotting factors leads to a bleeding tendency that is usually reversed by oral administration of vitamin k.
It is commonly used for prevention and treatment of vte prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation anticoagulation for mechanical prosthetic heart valves and myocardial infarction prevention in coronary artery disease. Warfarin 4 hydroxycoumarin inhibits the synthesis of vitamin k dependent coagulation factors including factors ii vii ix and x as well as proteins c and s. Studies of structure function relationships are the most advanced for the blood coagulation proteins. Vitamin k is important in the steps involving protein factor ii vii ix and x 1.