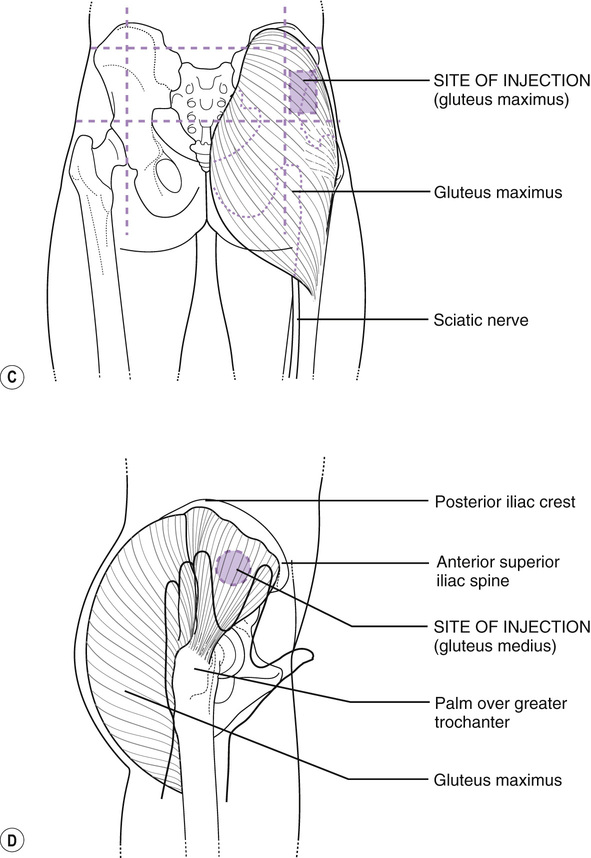
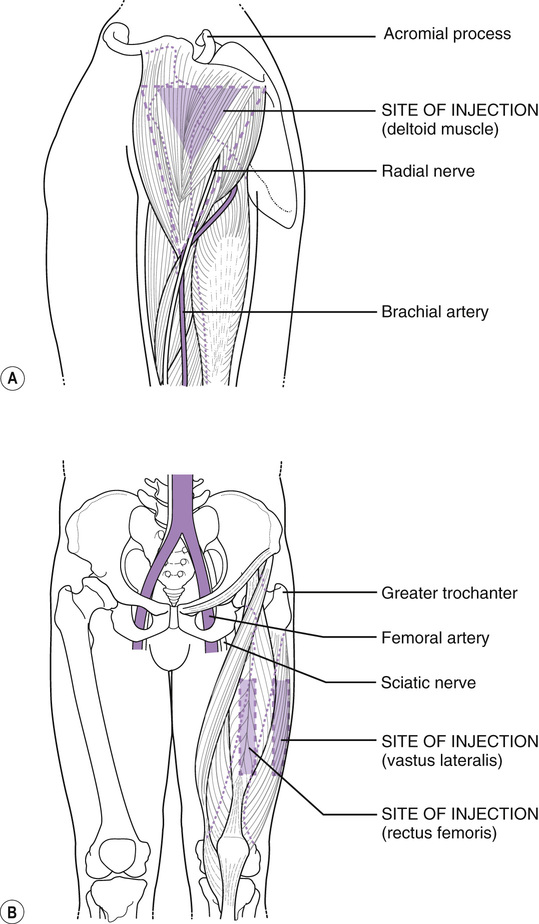
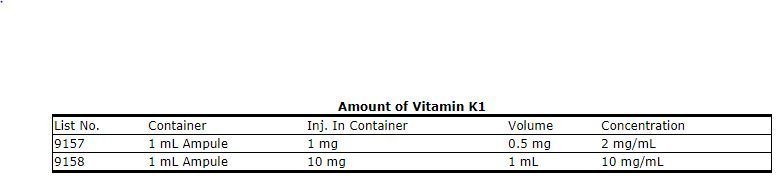
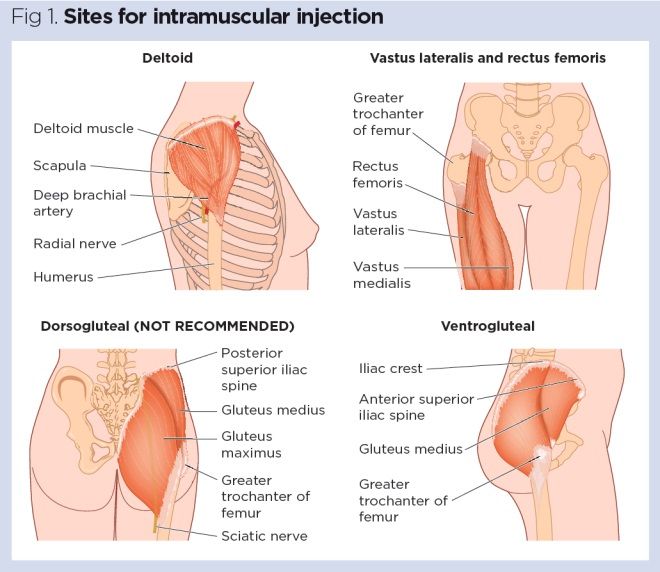
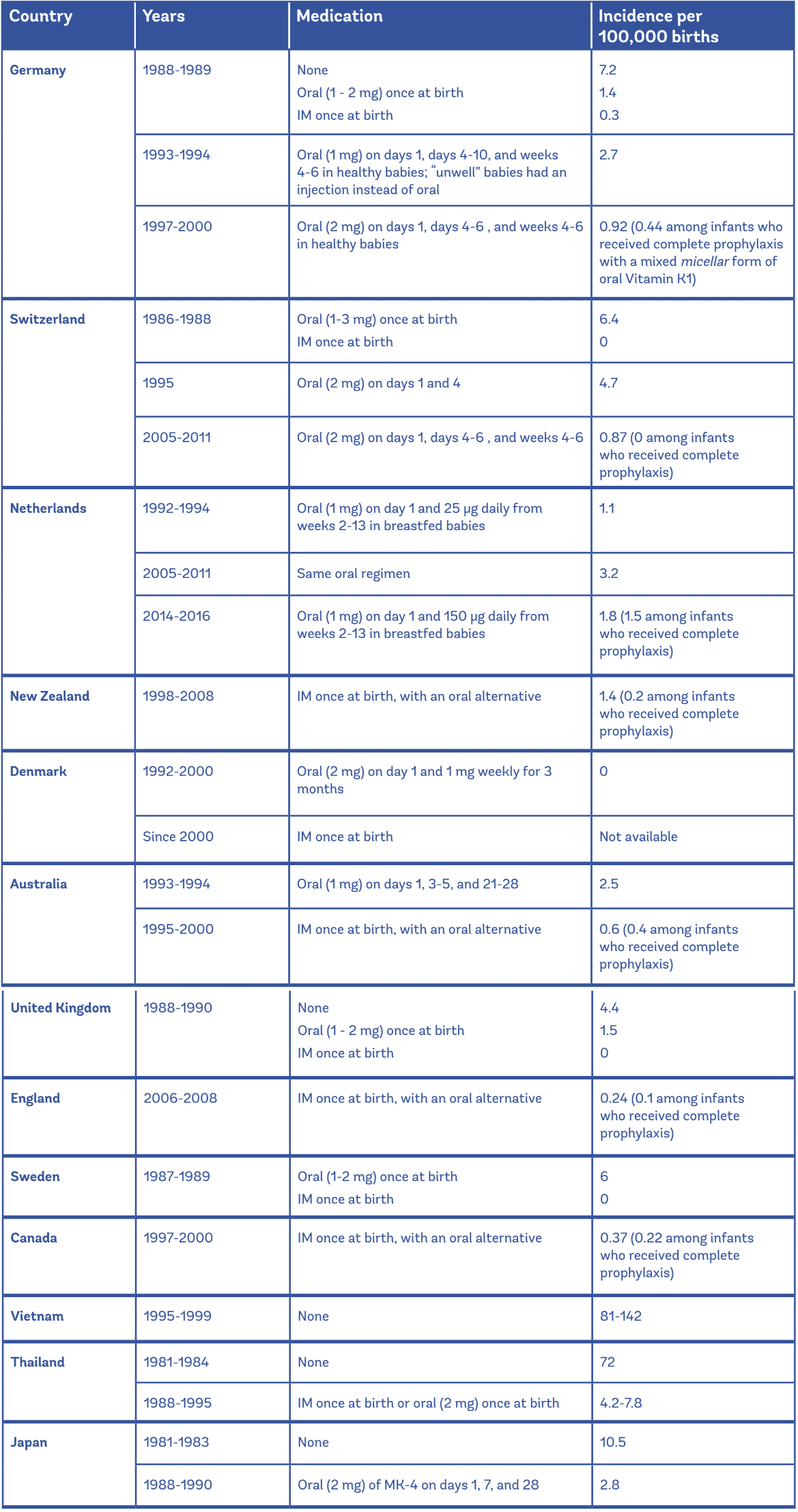
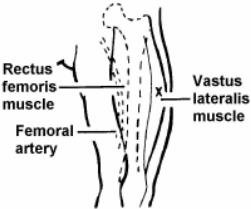
Vitamin K Im Injection Site Adults

Inr reduction observed within 24 48 hr monitor inr and give additional vitamin k if needed.
Vitamin k im injection site adults. Usual pediatric dose for hypoprothrombinemia not associated with anticoagulant therapy. In blood plasma 90 of vitamin k 1 is bound to lipoproteins. Following an intramuscular dose of 10 mg vitamin k plasma concentrations of 10 20 mcg l are produced normal range 0 4 1 2 mcg l. Vitamin k deficiency is rare in adults because many of the foods we eat contain adequate amounts of k1 and because the body makes k2 on its own.
Plus the body is good at recycling its existing. For the treatment of hypoprothrombinemia due to other causes. For injection dosage form. Children use is not recommended.
The initial recommended dose is 2 5 mg to 25 mg or more rarely up to 50 mg. A single injection of vitamin k for newborns is standard. Vitamin k1 injection phytonadione injectable emulsion usp aqueous dispersion of vitamin k1 for parenteral injection possesses the same type and degree of activity as does naturally occurring vitamin k which is necessary for the production via the liver of active prothrombin factor ii proconvertin factor vii plasma thromboplastin component factor ix and stuart factor factor x. 0 5 to 1 mg im once within one hour of birth use.
Adults and teenagers the usual dose is 2 5 to 25 milligrams mg rarely up to 50 mg. For the treatment of anticoagulant induced prothrombin deficiency. 2012 accp guidelines recommend vitamin k1 po dose not specified. Adults and teenagers the usual dose is 2 5 to 25 mg rarely up to 50 mg injected under the skin.
Minor bleeding any elevated inr. Usual pediatric dose for vitamin k deficiency. The dose may be repeated if needed. Vitamin k is also used to counteract an overdose.
While vitamin k deficiencies are rare in adults they are very common in newborn infants. 1 mg subcutaneously or im. Systemic availability following intramuscular administration is about 50 and elimination half life in plasma is approximately 1 5 3 hours. Prophylaxis and therapy of hemorrhagic disease of the newborn when caused by deficiency or interference with vitamin k activity.
The initial recommended dose is 2 5 mg to 10 mg or up to 25 mg by mouth rarely 50 mg. For problems with blood clotting or increased bleeding. Inr 10 no bleeding. Consider 2 5 5 mg po once.
Therefore vitamin k should be injected into a muscle or vein only when it cannot be given by injection under the skin or taken by mouth or when your doctor has judged that the benefit is greater.